Hormonal Birth Control: The Pill, Injections, and Emergency IUDs
Hormonal birth control—or, more accurately put, hormonal methods of birth control—all do essentially the same thing, which is that they interfere with your natural hormone levels to trick your body into not getting pregnant.
There are several types of hormonal birth control methods available from Women’s Clinic of Atlanta, each one offering its own benefits:
Birth Control Pills
The birth control pill is the most common form of hormonal birth control and offers 99% effectiveness if taken correctly. Out of the 72 million women in the US between the ages of 15 and 49, 14% rely on the pill to protect them from pregnancy.
There are two variations of the birth control pill: combination pills and progestin-only pills.
Combination Pills
As the name suggests, combination pills combine synthetic versions of two hormones, estrogen and progestin. These are the most commonly prescribed types of birth control pills.
Progestin-Only Pills
Progestin-only pills, often called POPs, do not include estrogen in the formula, just progestin. This type of pill is primarily for women who cannot medically take combination pills, but they are also available to women who would rather not take estrogen. Patients who should take progestin-only pills include those who are currently breastfeeding and those with a history of migraine headaches and blood clots.
How Do Birth Control Pills Work?
Whether your pill is combination or progestin-only, the hormone or hormones imitate your system’s natural hormones and interfere with certain reactions or events in your reproductive system.
With combination pills:
- Your hormone levels become stabilized, preventing your system from ovulating. Fluctuating hormone levels are what trigger ovulation and menstruation. So, if your hormone levels remain stable, your ovaries never receive the signal to release the egg.
- Even though no egg is released, the mucus in your cervix thickens up significantly, adding additional protection and preventing sperm from being able to reach an egg.
- Your uterine lining, which is naturally thick, becomes thin. Again, although no egg is released and sperm cannot pass through to the uterus, a thinned lining makes it more difficult for a fertilized egg to implant on the uterine wall and begin growing.
- Note that all three of these interferences are dependent upon continuous pill use. It’s crucial to take your pill every day at the same time so your body maintains the same hormone levels. Taking your pill even a few hours after your normal medication time can cause your levels to begin to fluctuate, opening you up to the possibility of an egg being released, your cervical mucus not thickening up enough, or your uterine lining not thinning out enough.
With progestin pills, some brands prevent ovulation, too, but all cause your mucus to thicken up enough to prevent sperm from passing through to your uterus. Continuous pill use is just as crucial for progestin-only pills as it is for combination pills.
How Effective Are Birth Control Pills?
When taken every day at the same time, all types are 99% effective at keeping you from becoming pregnant. If you are inconsistent with taking your pill, the effectiveness decreases.
For combination pills, if you miss a day or take your pill at noon one day and midnight the next, you can expect up to a 10% drop in protection. If you miss two days of birth control pills, especially in the first week of a new pack, you should use backup protection for seven days and begin a new pack of pills.
For progestin-only pills, if you miss taking your pill by even three hours, you should take it as soon as you can and use backup protection for at least two days to be safe.
Depo-Provera Injections
A Depo-Provera injection is an injectable version of progestin-only birth control. Its effects are similar to the pill in that it prevents the possibility of pregnancy.
How Does Depo-Provera Work?
Depo-Provera works by injecting a dose of progestin, which interferes with your reproductive system’s natural processes:
- The ovaries are not triggered to release an egg.
- Your cervical mucus thickens up enough to prevent sperm from reaching an egg in case one does make its way out of the ovary.
Women on Depo-Provera receive injections every three months.
How Effective Is Depo-Provera?
Depo-Provera is highly effective if injections are applied every three months. Since women do not have to keep up with pills and risk the possibility of skipping a pill here and there, injections can offer more than 99% effectiveness.
Emergency IUDs
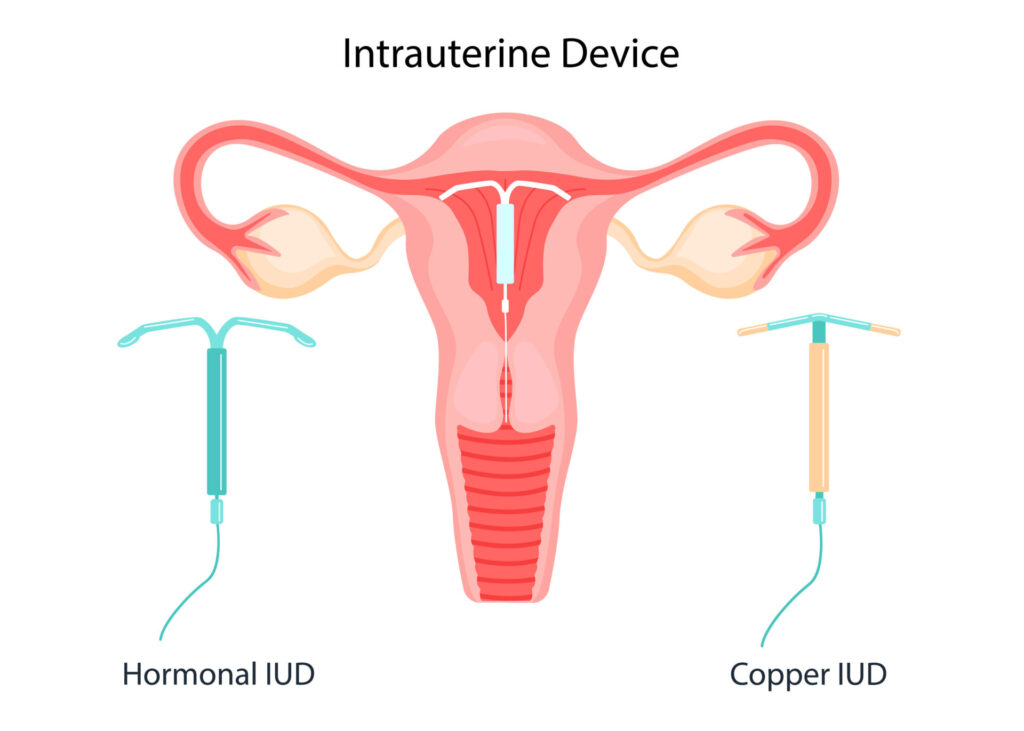
An emergency IUD is available as a form of contraception and lowers your risk of pregnancy if implanted within five days of unprotected sex. And the best part is that once inserted, the IUD provides years of protection against pregnancy.
How Does an IUD Work?
Whether your IUD is copper or hormonal, either works to keep sperm from reaching an egg.
A copper IUD repels sperm, redirecting them away from both the implant and any released eggs.
A hormonal IUD releases certain hormones to interfere with your reproductive system. Some hormonal IUDs thicken cervical mucus to prevent sperm from passing through. Some prevent the ovaries from releasing an egg. And some do both.
How Effective Are IUDs?
Both copper and hormonal IUDs are more than 99% effective at preventing pregnancy. Similar to Depo-Provera injections, IUDs do not require you to take a pill, so there is no room for missed protection or a decrease in effectiveness.
If you want to learn more about your options with hormonal pith control, you can schedule an appointment with Women’s Clinic of Atlanta.
Our team will provide a sexual wellness screening, speak with you about your needs, and discuss the best birth control options for you. We offer birth control pills, Depo-Provers injections, and emergency IUDs to shield you against pregnancy.
Schedule a birth control appointment by texting “appointment” to 404-777-4771 today.
Women’s Clinic of Atlanta is HIPAA compliant and AAAHC accredited.
Recent Articles:
